What Is an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple, non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart over several beats. Small electrodes placed on the chest, arms, and legs detect the electrical signals generated by the heart. These signals are then displayed as a graph, giving doctors detailed insights into the heart’s function and rhythm.
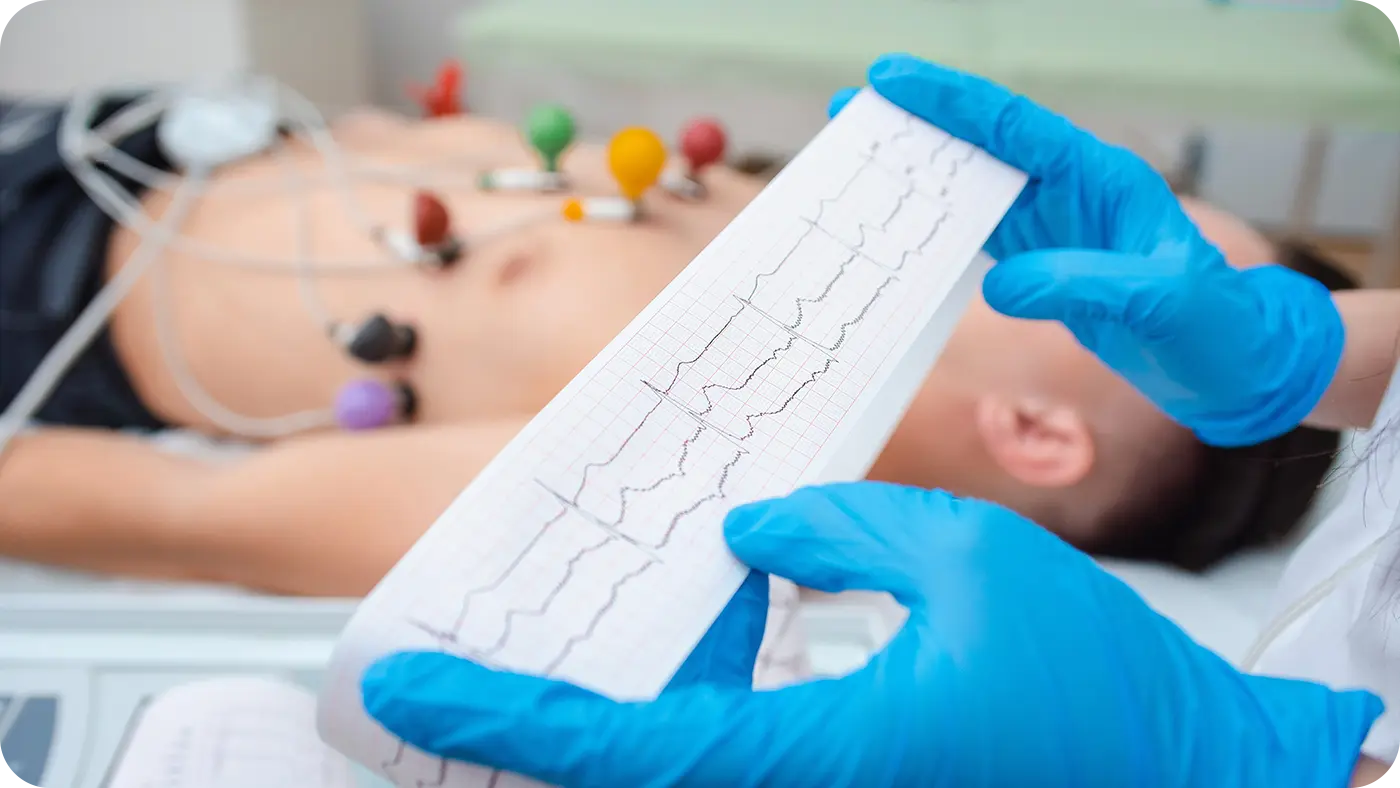
Why Is an Electrocardiogram Important?
An EKG plays an essential role in:
- Detecting Arrhythmias: Helps identify abnormal heart rhythms, such as tachycardia or bradycardia.
- Diagnosing Heart Block: Pinpoints problems with the heart’s electrical conduction system.
- Assessing the Heart After a Heart Attack: Shows how a heart attack may have damaged the heart muscle.
- Monitoring Medication Effects: Checks if certain medications are affecting the heart’s function.
- Response to Stress or Exercise: Stress EKGs reveal how the heart responds to physical effort, which helps diagnose angina or other conditions.
When Is an EKG Recommended?
- Heart-Related Symptoms: If you have chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, fainting, or shortness of breath.
- Routine Monitoring: For patients with a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
- Medication Monitoring: To check for any side effects that may impact the heart.
- Before Surgery: To ensure your heart can handle the stress of anesthesia and surgery.
- Heart Disease Screening: For people with a family history or other risk factors.
- After a Heart Attack: To monitor recovery and watch for complications.
- Older Adults: As part of general check-ups, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
- Athletes: Especially those in competitive sports, to rule out hidden heart conditions that could pose risks during intense activity.
An EKG is quick, painless, and provides essential information for diagnosing and managing heart conditions.
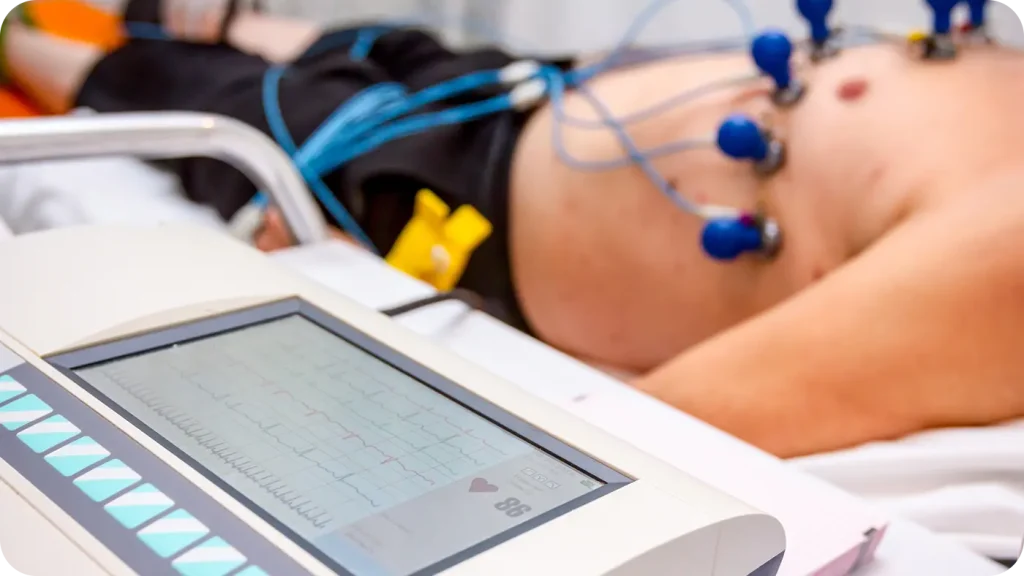
Types of EKG
- Standard (Resting) EKG: Uses 12 electrodes on the chest, arms, and legs. The patient remains still while the heart is monitored for a few minutes. It can detect arrhythmias, ischemia, or previous heart attacks.
- Holter EKG: Records the heart’s activity for 24–48 hours using a portable device, capturing irregularities that may not appear during a standard EKG.
- Stress EKG (Cardiac Stress Test): Monitors the heart during exercise on a treadmill or bike to detect issues that occur only under stress.
- 3-Lead EKG: A simplified version using three electrodes, often for quick checks in emergencies.
- 5-Lead EKG: Uses five electrodes, commonly for continuous monitoring in ICUs or ambulances.
- High-Resolution EKG: Provides detailed readings for subtle abnormalities, mostly used in research or complex cases.
Conclusion
Each type of EKG serves a specific purpose, chosen according to your doctor’s assessment of your heart health. For more details about costs and to schedule an EKG, please consult our specialists.
Recommended Articles
Frequently asked questions
What is the price of an EKG?
- Cardiology consultation + EKG + echocardiogram: 520–550 RON
- EKG with interpretation: 120 RON
- Pediatric cardiology consultation + EKG + echocardiogram: 620 RON
Can a heart attack be seen on an EKG?
Yes, an EKG can show signs such as ST segment elevation or pathological Q waves, indicating a heart attack.
How long does an EKG take?
A standard EKG usually takes 5 to 10 minutes.
What are normal EKG values?
- Heart rate: 60–100 beats per minute
- PR interval: 120–200 milliseconds
- QRS complex: less than 120 milliseconds
- ST segment: isoelectric
- QT interval (QTc): under 440 milliseconds in men, under 460 milliseconds in women
- P wave: under 120 milliseconds and less than 2.5 mm in height
- Normal adult heart rate: 60–100 beats per minute