Every woman of reproductive age, meaning after puberty and before menopause, will develop cysts on her ovaries. These cysts differ in size, shape, and appearance, but most are harmless and functional. The term “ovarian cyst” often creates anxiety among women, though many cysts play a regular role in ovulation. Understanding what cysts are and how they form can reduce unnecessary concern.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
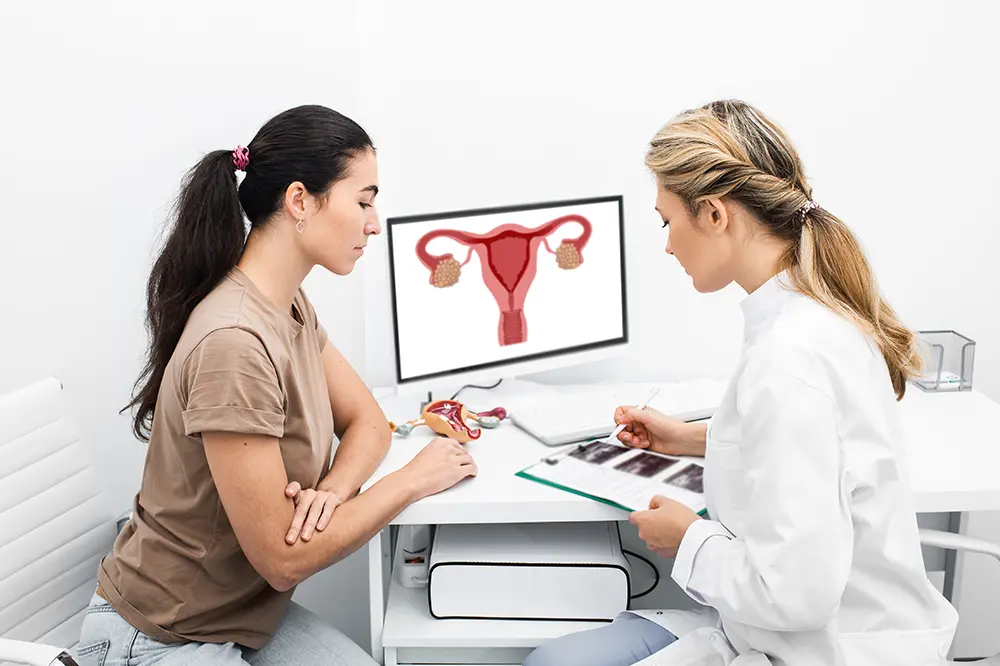
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form inside or on the surface of an ovary. The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system, located on either side of the uterus in the lower abdomen. Each ovary has the role of producing eggs and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Most women will experience cyst formation at some point, often without symptoms or complications.
In many cases, cysts remain small and harmless, resolving on their own. Sometimes, however, a cyst grows larger or persists, leading to symptoms that require medical assessment. Cysts may be discovered incidentally during a gynecological examination. This is why regular check-ups are recommended throughout reproductive life.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are classified into several categories, with functional cysts being the most common. Functional cysts are part of the menstrual cycle and include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts. Follicular cysts form when a follicle fails to release an egg, while corpus luteum cysts occur when fluid accumulates in the follicle after the egg is released. Both types are usually temporary and benign.
Other cysts may develop outside regular ovulation. Dermoid cysts contain tissue such as hair or fat. Cystadenomas are noncancerous growths on the ovary’s outer surface. Endometriomas form when uterine tissue attaches to the ovary, often associated with endometriosis.
How Do We Know If We Have Ovarian Cysts?
Many ovarian cysts cause no symptoms and are found only during routine gynecological visits. Because of this, yearly examinations after the onset of sexual activity are recommended. As cysts enlarge, however, women may notice signs such as abdominal bloating, pelvic discomfort, or changes in the menstrual cycle. Painful intercourse, breast tenderness, nausea, or vomiting can also appear.
Some symptoms indicate urgent care is needed. Severe pelvic pain, fever, dizziness, or rapid breathing may suggest a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion. Both conditions block normal blood flow and can have serious consequences if untreated. Immediate consultation with a specialist is essential in such cases.
Ovarian Cyst Treatment
Treatment depends on the size, type, and persistence of the cyst. Small cysts are often monitored, as many disappear naturally. Birth control pills may be prescribed to regulate ovulation and prevent new cysts from forming. They also provide protective benefits, such as lowering ovarian cancer risk.
Surgical options are considered when cysts grow, persist, or raise concern for malignancy. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used for smaller cysts. A laparotomy, requiring a larger abdominal incision, is reserved for larger or suspicious cysts. If malignancy is confirmed, hysterectomy may be necessary to remove reproductive organs.
Early diagnosis is key, as smaller cysts can often be removed laparoscopically. Laparoscopy reduces risks of infection, blood clots, and complications compared to open surgery. Recovery is faster, postoperative pain is reduced, and damage to surrounding structures is minimized. For these reasons, it is the preferred method when feasible.
Ovarian Cysts and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a frequent condition where many small cysts form in the ovaries. The condition is linked to hormonal imbalance, which interferes with regular ovulation. PCOS can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, reduced fertility, weight gain, excess hair growth, and acne. Left untreated, it may result in long-term complications, including infertility.
More than half of women may experience this syndrome, making a timely gynecological evaluation essential. Management focuses on controlling symptoms, restoring hormonal balance, and preserving fertility. Lifestyle changes and medical treatments can improve long-term health outcomes. A gynecologist consultation is crucial to avoid serious complications.
VenArt Clinic specializes in gynecological surgery and gynecological oncology. Our team combines advanced surgical expertise with modern medical technologies. We are committed to offering high-quality care and excellent long-term results for women’s health conditions. For more details, please visit our gynecological oncology section. Schedule a consultation and find out how we can help.