Introduction
At VenArt Clinic, we are committed to providing you with clear, reliable information so you can make informed decisions about your vascular health. In this article, you will learn what subclavian arteries are, why they matter, and how conditions affecting them can be treated safely and effectively.
Our experienced team, including Prof. Dr. Jérôme Cau — a leading expert in vascular surgery — combines advanced medical techniques with personalized care plans. We offer a welcoming environment, thorough consultations, and state-of-the-art technology to ensure your safety and comfort.
What Are Subclavian Arteries And Why Are They Important?
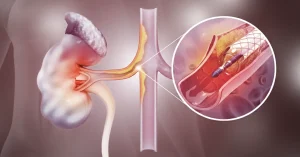
The subclavian arteries are two major blood vessels that supply blood from the heart to your upper limbs and parts of your brain. When these arteries become narrowed — a condition known as stenosis — the tissues and organs in these areas receive less blood, which can lead to serious health problems. The main cause of stenosis is atherosclerosis, which occurs when fatty deposits build up on the artery walls and restrict blood flow.
Causes Of Subclavian Artery Stenosis And Risk Factors
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of subclavian artery stenosis, but other conditions like arteritis (inflammation of the artery walls) and compression syndromes can also play a role. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and obesity, all of which increase the chance of artery narrowing. If you have any of these risk factors, regular check-ups are crucial. Preventive screening offered at VenArt Clinic can help detect problems early and guide you to the right treatment plan.
Diagnosis Of Subclavian Artery Stenosis
Your doctor may suspect subclavian artery stenosis if there is a significant difference in pulse or blood pressure between your arms, usually over 20 mmHg. Other signs include abnormal sounds (murmurs) in the neck or changes in the upper limbs, such as finger necrosis or small nail bed hemorrhages. If an inflammatory condition like vasculitis is suspected, blood tests such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be done.
Arterial Doppler ultrasound is a valuable, non-invasive tool that reveals vascular changes linked to stenosis. Additional imaging tests like MRI, angio-MRI, CT, angio-CT, arteriography, or aortography provide detailed insights when more information is needed.
Treatment Of Subclavian Artery Stenosis
Treatment depends on the severity and progression of the condition. It often begins with medication to manage contributing factors. When needed, minimally invasive methods like angioplasty and stenting are used to restore proper blood flow. If these methods are not enough, surgery may be considered as a last resort. This involves bypassing the narrowed segment with a healthy vessel portion — possible techniques include carotid-subclavian, aorto-subclavian, or axillo-axillary bypass, depending on the case.
What Is Angioplasty And How Does It Help Treat Subclavian Arteries?
Subclavian artery angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that takes about one hour. It may be recommended if you have symptoms such as:
- Severe fatigue and difficulty with physical activities
- Arm pain that worsens with effort
- Cold sensation in the arms or finger necrosis
- Neurological signs like dizziness, blurred vision, or loss of balance
For What Situations Is Angioplasty Recommended?
Angioplasty is commonly used for:
- Symptomatic ischemia
- Subclavian artery steal syndrome (when blood flow is diverted from other arteries)
- Severe arm claudication
- Preserving blood flow in the mammary artery before coronary bypass surgery
- Post-bypass surgery if signs of ischemia appear
- Dialysis or axillary graft patients
- Blue finger syndrome due to finger necrosis
- Inability to measure blood pressure accurately
- Reducing the risk of blood clots affecting the brain
When no symptoms are present, interventional treatment may be needed to maintain healthy blood flow to the brain or during other vascular procedures, especially if other large arteries above the aortic arch are affected.
How Do You Prepare For Angiography And Angioplasty?
Preparation steps include:
- Blood tests to check organ function and safety.
- Electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to assess heart health.
- Stopping certain medications as advised by your doctor.
- Fasting before the procedure.
- Avoiding smoking temporarily to lower complication risks.
How Does Subclavian Artery Angioplasty Proceed?
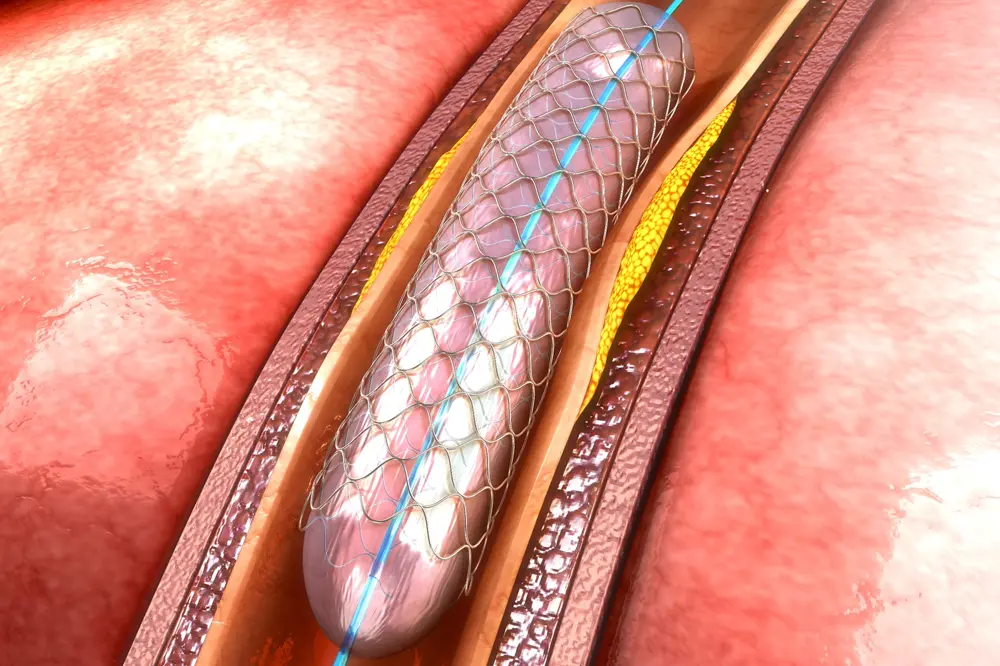
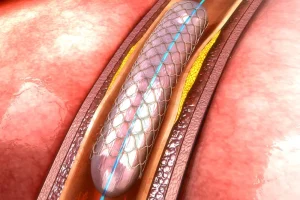
Performed in a specialized angiography suite under local anesthesia, the procedure involves a small incision through which a catheter and a tiny balloon are inserted to open the narrowed artery. A stent is then placed to keep the artery open. Throughout the procedure, your vascular team monitors progress carefully to ensure safety and success.
How Long Does Hospitalization Last?
After angioplasty, you will stay under observation for monitoring. Most patients return home within one to two days and can resume normal activities soon after, following medical advice. Initial rest, especially avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activity, is recommended for a safe recovery.
What Is Recovery Like After The Procedure?
After the procedure, you will be moved to an observation area where your doctor will monitor your condition and check for any complications. Mild pain or discomfort at the insertion site is normal and usually resolves quickly. Follow all post-procedure advice to ensure smooth healing.
What To Keep In Mind After Angioplasty?
For several weeks, avoid intense physical activities, heavy lifting, or contact sports. Monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol closely. Maintain a balanced diet and healthy body weight, and follow all medical recommendations for long-term vascular health.
Risks Of Angiography/Angioplasty
Although rare, possible complications include:
- Allergic reactions to medications or contrast agents
- Reactions to anesthetics
- Minor bleeding at the puncture site
- Arteriovenous fistula at the access point
- Fever or headache
- Infection
- Gas embolism
- Injury to the aortic wall or target artery
- Aortic rupture or dissection
- Restenosis within the stent
- Stent migration
- Distal embolization (clots traveling to other vessels)
- Neurological events such as transient ischemic attack, stroke, hemiplegia, or double vision
At VenArt Clinic, your safety is our top priority. We use the latest technology and provide close monitoring during every stage of your treatment to keep risks minimal.
Schedule A Consultation
Your vascular health deserves the best care. If you have questions about subclavian artery angioplasty or want to discuss your treatment options, our specialists are here to help. Talk to us today.
Sources:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28887261
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/0741-5214(85)90184-3/fulltext
Medical consultant: Prof. Dr. Jérôme Cau