Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
Choose the modern, minimally invasive solution to restore blood flow
Home » Vascular and Endovascular Surgery » Post-thrombotic Syndrome
Medical Procedures
Vascular Techniques
Endovascular Techniques
Conditions Treated

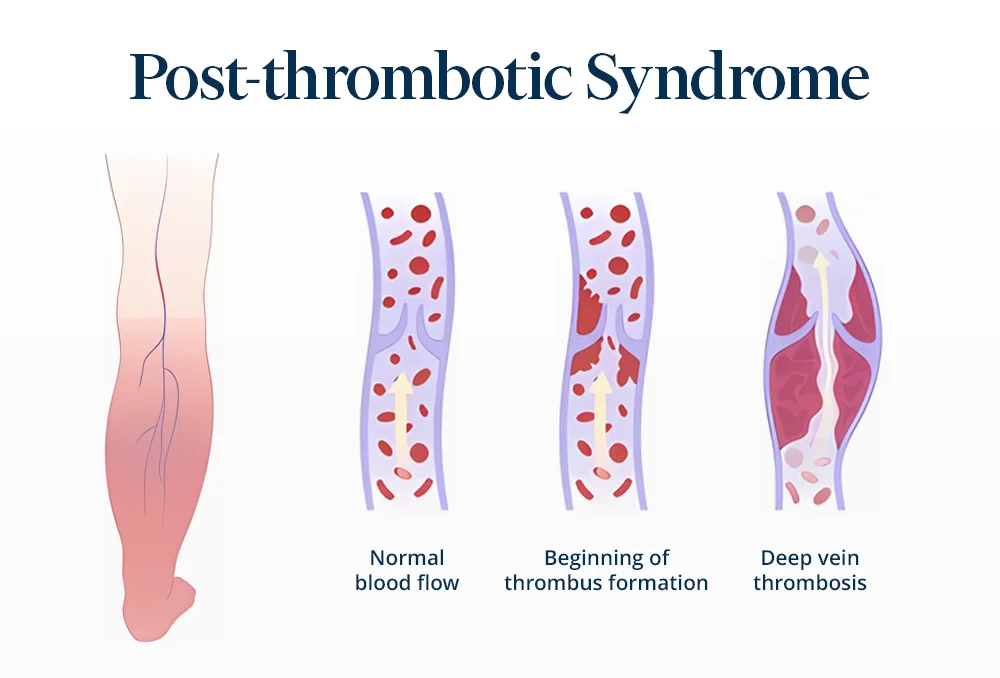
What is post-thrombotic syndrome?
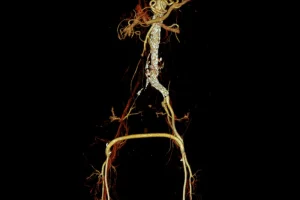
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), also known as post-phlebitic syndrome, is a common chronic complication that occurs following deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It is estimated to affect between 20% and 50% of patients who have suffered a DVT, particularly in the first two years after diagnosis, with severe cases occurring in 5% to 10% of cases.
This condition occurs when a blood clot affects the valves and walls of the deep veins, leading to poor blood circulation back to the heart. This causes increased pressure in the veins (venous hypertension) and blood accumulation in the affected limb. Over time, this situation can significantly reduce quality of life, limit daily activities, and lead to additional medical expenses.
Book an Appointment
Who is this procedure for?
The procedure is recommended for patients suffering from post-thrombotic syndrome caused by deep vein thrombosis, even if the thrombosis occurred several years ago.
It is indicated for people with persistent symptoms such as:
- Pain
- Swelling of the legs
- Heaviness in the affected limb
- Skin changes
- Appearance of venous ulcers
What are the signs of post-thrombotic syndrome?
- The manifestations of post-thrombotic syndrome usually appear in the area of the limb affected by deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and can vary in intensity from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include:
- Persistent discomfort or dull pain, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or severe fatigue in the affected limb
- Localized edema (swelling)
- Muscle spasms, cramps, or tingling sensations
- Skin that becomes red, irritated, or changes color
- Sensory disturbances similar to fine pricks (“pins and needles”)
- In severe cases, skin thickening, visible vein dilations (varicose veins), or venous ulcers may occur
Advantages of treatment for post-thrombotic syndrome
Symptom relief
Minimally invasive treatment can significantly reduce—and sometimes even completely eliminate—clinical manifestations such as swelling, pain, or heaviness in the affected limb.
Improved venous circulation
Using modern techniques, effective blood flow can be restored in areas affected by thrombosis, promoting normal vein function.
Prevention of complications
The treatments applied help to avoid serious long-term problems such as venous ulcers and other consequences of chronic circulatory insufficiency.
Fast and comfortable recovery
As this is a minimally invasive procedure, recovery time is short and the impact on daily activities is minimal.
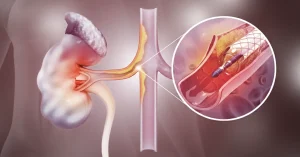
When is venous stenting recommended?
This procedure is particularly recommended for patients who:
- Have severe forms of post-thrombotic syndrome that cannot be controlled by conservative methods (e.g., compression stockings or medication)
- Have significant venous stenosis (narrowing or blockage of a vein) in the area affected by DVT
- Have persistent or worsening symptoms that affect circulation and quality of life
Patient preparation
Before the procedure, a detailed medical evaluation is essential, which may include:
- Doppler ultrasound: to visualize how blood flows through the veins and to locate any obstructions
- Clinical consultation: involves assessing symptoms and medical history
- Blood tests: to rule out other conditions or risks associated with the procedure
How is the procedure performed?
Vein stenting is an image-guided endovascular procedure that involves the following steps:
- Local anesthesia or mild sedation:
- The patient remains conscious, and the procedure is performed under conditions of increased comfort.
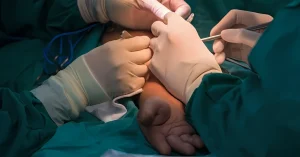
- Access to the venous system:
- A small incision is made in the groin or in the area of the affected vein, through which a thin catheter is inserted.
- Guided navigation:
- The catheter is guided using imaging technologies (X-ray, fluoroscopy, ultrasound) to the area of stenosis or blockage.
- Dilation of the affected area:
- If a significant narrowing is identified, it can be treated with an angioplasty balloon to open the vein.
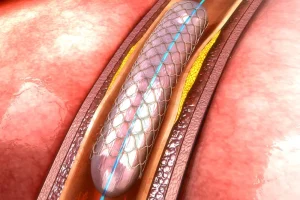
- Stent placement:
- A stent—a small cylinder made of metal or biocompatible material—is inserted into the affected area to keep the vein open and prevent the blockage from recurring. The stent remains in place permanently and supports normal circulation.
- Checking effectiveness:
- After placement, the doctor checks whether blood flow has been restored and whether the procedure was successful, often using another Doppler ultrasound.
Post-procedure recovery
After the procedure, the patient will be monitored for several hours to ensure that there are no complications (such as bleeding or adverse reactions). Patients can usually go home the same day or after a short hospital stay, depending on their condition.
During recovery:
- Anticoagulant medication may be recommended to prevent blood clots from forming.
- The patient will need to follow a regimen of light exercise and avoid prolonged standing or sitting.
- Regular visits to the doctor will be necessary to monitor progress and confirm the success of the procedure.
Effectiveness and prognosis
Minimally invasive stenting can significantly improve the symptoms of post-thrombotic syndrome, reducing pain, swelling, and heaviness in the lower limbs. Restoring blood flow can also prevent the formation of venous ulcers and other long-term complications.
However, long-term success depends on following medical recommendations and properly managing your overall health.
In conclusion, minimally invasive stenting is a valuable option in the treatment of post-thrombotic syndrome when conservative approaches are not effective.
Risks of post-thrombotic syndrome
Although minimally invasive methods reduce the risks associated with traditional interventions, there are still some minimal risks, such as:
- Temporary discomfort at the site of the intervention
- Allergic reactions to anesthetics or materials used
- Risk of new blood clots forming (minimal, but present)
- Minor infections at the puncture site
Why choose the VenArt Clinic?
At the VenArt Clinic, we treat post-thrombotic syndrome using minimally invasive methods, using the technique of stenting the affected veins, which allows blood flow to be restored without major surgery.
Regardless of the duration of the thrombosis, our specialists can offer customized solutions for each patient. The benefits of treatment at our clinic include:
- Extensive experience and modern equipment
- Minimally invasive procedures with quick recovery
- Team of specialists recognized in the field of vascular surgery
- Personalized approach for each patient
Schedule your consultation now!
If you suffer from post-thrombotic syndrome and want an effective and modern solution, schedule a consultation at VenArt Clinic!
Medical Team
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes post-thrombotic syndrome?
The main cause of post-thrombotic syndrome is the formation of a blood clot in the deep veins, which leads to impaired blood flow and damage to the veins, resulting in chronic symptoms.
How is post-thrombotic syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by a detailed clinical evaluation, Doppler ultrasound and, in some cases, phlebography to analyze the blood flow and structure of the affected veins.
Is it necessary to wear long-term compression stockings?
Yes, compression stockings are essential for managing symptoms and preventing post-thrombotic syndrome from worsening. They help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Can I exercise if I have post-thrombotic syndrome?
Yes, light exercise such as walking is beneficial for improving circulation and reducing symptoms.
Can post-thrombotic syndrome lead to venous ulcers?
Yes, in severe cases, post-thrombotic syndrome can lead to venous ulceration, which requires specific treatment.
Is post-thrombotic syndrome a permanent condition?
PTSD is a chronic condition, but symptoms can be effectively managed with appropriate treatments. In some cases, symptoms may persist long-term.
How can I prevent recurrence of thrombosis?
Preventing recurrence of thrombosis is done by using anticoagulants, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding a sedentary lifestyle and wearing compression stockings.
How long does recovery take after treatment for post-thrombotic syndrome?
Recovery depends on the severity of the case and the treatments applied. The patient can usually see significant improvements in a few weeks or months, but long-term management is necessary.