Thrombectomy
Choose the modern solution to restore blood flow
Home » Vascular and Endovascular Surgery » Thrombectomy
Medical Procedures
Vascular Techniques
Endovascular Techniques
Conditions Treated
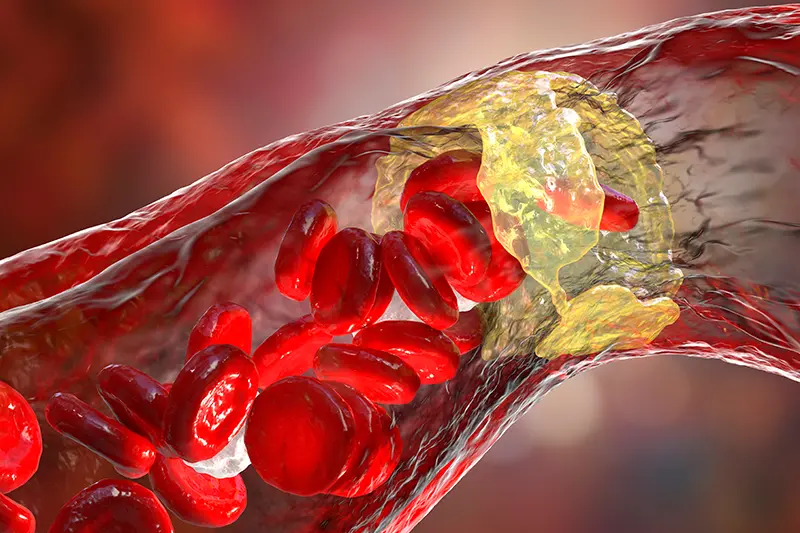
Do you need a fast and effective solution to remove blood clots and restore circulation? The Thrombectomy procedure is a minimally invasive technique that offers a modern alternative to traditional surgery.
Request an appointment
What is a Thrombectomy?
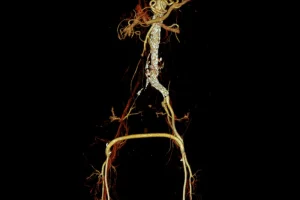
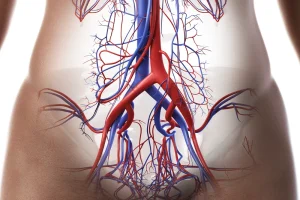
Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove blood clots (thrombi) from blood vessels. This technique is often used to treat arterial or venous thrombosis, as well as ischemic strokes caused by a blocked blood vessel.
When a thrombectomy is recommended
Thrombectomy is recommended in the following situations:
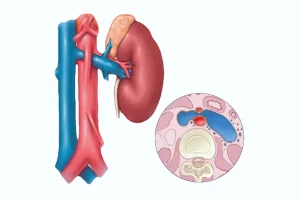
- Ischemic stroke caused by a thrombus blocking a cerebral artery;
- Acute thrombosis of the lower or upper limbs;
- Arterial emboli jeopardizing the irrigation and functioning of vital organs;
- Deep vein thromboses (DVT) that do not respond to drug treatment.
Benefits of thrombectomy
- Minimally invasive – no large incisions;
- Rapid recovery compared to traditional surgical methods;
- Reduced risk of postoperativecomplications;
- Rapid restoration of blood circulation to the affected area;
- Reduces the risk of permanent damage caused by ischemia.
How the Thrombectomy procedure works
1. Patient Preparation
- Blood tests and imaging investigations such as angiography or CT scans are performed to pinpoint the exact location of the thrombus;
- The patient is informed about the procedure and the risks involved;
- Local or general anesthesia is applied, depending on the complexity of the case.
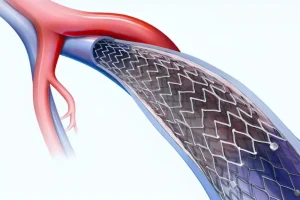
2. Catheter insertion
- A small puncture is made in the femoral or radial artery;
- Insert a special catheter guided by imaging (angiography) to the thrombus.
3. Thrombus Extraction
- Thrombectomy devices are used to capture and extract the blood clot;
- Sometimes a suction device may be used to remove the thrombus;
- Anticoagulant or thrombolytic medication is given if necessary to prevent new clots from forming.
4. Evaluation of Results
- A new angiogram is performed to verify that blood flow has been restored;
- Remove the catheter and apply a compression bandage at the puncture site.
Contraindications for Thrombectomy
The procedure is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Patients with active bleeding;
- Severe allergy to the contrast agents used;
- Severe blood clotting disease;
- Severe acute infections in the surgical site.
Why choose VenArt Clinic?
- Team of specialized doctors with extensive experience.
- Modern technology and innovative methods.
- Minimally invasive treatments for fast recovery.
- Personalized approach for each patient.
- Proven results and numerous success stories.
- Warm and professional atmosphere.
- Complete services in one location.
Medical Team
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a thrombectomy?
Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove blood clots (thrombi) from the cerebral arteries. It is mainly used in severe ischemic strokes to restore blood flow and limit damage to brain tissue.
How is the procedure performed?
The interventional doctor guides a catheter through the large arteries (usually through a groin artery) to the blocked artery in the brain. Using special devices (stent retriever or mechanical suction), the clot is trapped or suctioned and then removed, restoring normal blood circulation.
How long does thrombectomy take?
The length of the procedure varies, depending on the location and size of the clot as well as the patient’s anatomy, but in general it can take between 30 minutes and several hours.
What risks or complications may occur?
Like any invasive procedure, endovascular thrombectomy carries some risks, such as bleeding at the puncture site, intracranial hemorrhage, vascular damage, reactions to contrast agents or, in rare cases, worsening of neurological symptoms. However, the potential benefits usually outweigh the risks when the procedure is properly recommended.
What preparation is needed before the procedure?
The patient will be quickly and thoroughly evaluated by clinical examination, laboratory tests and imaging (CT, perfusion CT, MR angiography) to confirm the location and extent of the occlusion. In the emergency department, there are no special long-term preparations, but it is essential to present to hospital as soon as possible after the onset of stroke symptoms.
Is anesthesia given?
The procedure can be performed under sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and the decision of the medical team. The goal is to keep the patient comfortable and stable throughout the procedure.
How soon after the procedure?
Some patients may notice an improvement in symptoms during or immediately after the procedure, while others may take several hours or days to notice a significant recovery. The outcome depends on the severity of the initial stroke and the speed of the procedure.
Is additional treatment needed after thrombectomy?
Typically, the patient will continue a treatment regimen that may include antiplatelets, statins and other medications to control risk factors (blood pressure, diabetes, cholesterol) and prevent a new stroke episode. Lifestyle modification counseling (healthy diet, moderate physical activity, smoking cessation) is also very important.