Abdominal Eventration
Laparoscopic appendectomy
Home » General Laparoscopic Surgery » Abdominal Eventration
Medical Procedures
Laparoscopic Interventions
Classic Surgical Interventions
Abdominal Conditions
Pelvic and Perineal Conditions
Other Conditions
Abdominal hernia is a condition in which internal organs protrude through a defect in the abdominal wall, forming a visible bulge under the skin.
This can occur after previous surgery or due to weakening of the abdominal muscles.
Book an Appointment
Causes of abdominal eventration
Abdominal hernia develops when the abdominal wall does not heal properly after surgery, leading to a defect through which abdominal contents can protrude. The main causes include:
- Rupture of postoperative sutures;
- Poor healing of the scar;
- Weakening of the abdominal muscles.
The difference between hernia and eventration
- An abdominal hernia occurs spontaneously through a weak spot in the abdominal wall and is not related to previous surgery.
- Eventration is a postoperative complication that occurs at the site of a scar after abdominal surgery due to weakening of the abdominal wall.
Factors that contribute to the development of eventration
Several factors can contribute to the development of eventration, including:
- Intense physical exertion too soon after surgery;
- Repeated episodes of coughing that increase intra-abdominal pressure;
- Chronic constipation, which strains the abdominal wall;
- Postoperative infections, which affect the healing process;
- Obesity, which puts additional pressure on the abdominal wall.
Who is the abdominal hernia repair procedure intended for?
Surgery for abdominal eventration is recommended for patients who:
- Have a visible bulge in the abdomen that may increase in size;
- Experience discomfort or pain, especially during exertion;
- Are at risk of complications, such as strangulation of the intestine.
Benefits of abdominal eventration
- Elimination of pain and discomfort;
- Reduction of the risk of severe complications, such as intestinal obstruction;
- Restoration of abdominal wall functionality;
- Improvement of aesthetic appearance and quality of life.
Symptoms of abdominal eventration
Hernia develops gradually and can go through several stages:
- Uncomplicated: manifested by a protrusion at the scar site, without other symptoms;
- Incarcerated: the swelling becomes painful and difficult to return to the abdomen;
- Strangulated: characterized by intense pain, vomiting, and intestinal obstruction, requiring emergency surgery.
It is important for patients to follow their doctor’s recommendations for optimal recovery and to monitor any unusual postoperative symptoms.
When is surgery necessary?
Surgical treatment is the only effective solution for eventration, and surgery is recommended even in the early stages to avoid complications. Surgery can be performed using:
- The laparoscopic technique, used for small and medium-sized eventrations, which involves small incisions and the insertion of a mesh inside the abdominal wall;
- Open surgery, indicated for more severe cases, where an incision is made at the scar and a mesh is inserted to prevent recurrence.
How does the procedure work?
Abdominal hernia surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques (laparoscopy) or open surgery, depending on the size and complexity of the defect.
The surgeon will reinforce the abdominal wall using sutures and, in many cases, a special mesh to prevent recurrence.
Eventration surgery with mesh
Mesh repair involves placing a synthetic mesh in the defect area to strengthen the abdominal wall and reduce the risk of recurrence.
It can be placed either between the muscle layers (in classic surgery) or inside the abdominal cavity (in laparoscopy). The use of mesh provides safer healing and more effective recovery for the patient.
What should be done after the procedure?
- Follow the rest period recommended by your doctor;
- Avoid lifting heavy objects and intense physical exertion;
- Maintain a balanced diet to avoid constipation;
- Monitor your progress and attend regular medical check-ups.
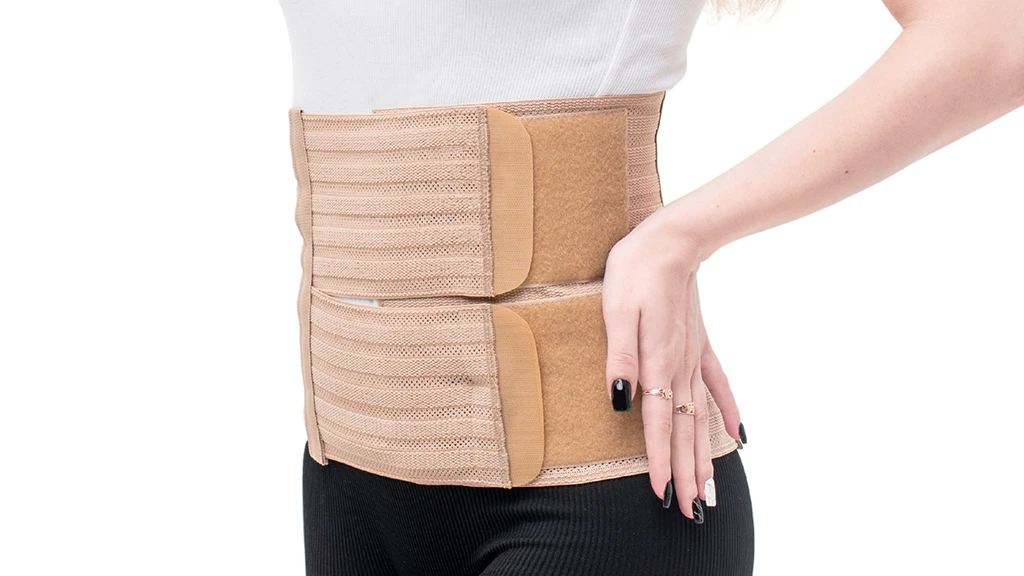
Abdominal belt for eventrations
It is a medical device used to support the abdominal wall, reduce discomfort, and prevent the worsening of hernia, especially before or after surgery.

How long does the hernia repair surgery take?
The duration of the operation varies depending on the size of the hernia, the technique used, and the presence of any complications.
- Laparoscopic surgery takes, on average, 1-2 hours, being faster and less invasive;
- Traditional surgery can take between 2 and 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the case and the size of the defect to be corrected.
Regardless of the method used, the success of the intervention depends on the surgeon’s experience and compliance with postoperative recommendations.
Recovery after classic hernia repair and laparoscopic surgery
Recovery after hernia surgery depends on the type of procedure and the size of the defect treated.
Recovery after classic hernia surgery
- Hospitalization lasts between 3 and 7 days, depending on the complexity of the case;
- Postoperative pain may be more intense, but it is managed with painkillers;
- Light activities can be resumed after 4-6 weeks, and intense physical exertion should be avoided for at least 3 months;
- Wearing an abdominal belt to support the abdominal wall during recovery is recommended;
- Medical check-ups are essential for monitoring healing.
Recovery after laparoscopic hernia repair surgery
- Hospitalization is shorter, generally 1-3 days;
- Pain is reduced due to small incisions;
- The patient can resume normal activities after 2-4 weeks, but must avoid strenuous physical activity for at least 6-8 weeks;
- There is a lower risk of infection and complications compared to traditional surgery.
Why choose VenArt Clinic?
- Experienced medical team: Specialists with years of practice in general laparoscopic surgery, with proven results and numerous positive testimonials;
- Modern technology: We use minimally invasive methods, such as laparoscopic surgery, for quick recovery and reduced discomfort;
- Personalized approach: Each patient is unique, and the treatment plan is tailored to their needs for a safe and effective medical experience;
- Comprehensive post-operative care: We provide guidance throughout recovery, careful monitoring, and answer any questions to ensure a complication-free healing process.
Schedule a consultation now!
If you have been diagnosed with abdominal eventration, don’t wait until complications arise! Schedule a consultation for a safe and effective solution.
Fill out the form below or call us to schedule a personalized consultation.
Our specialists will answer all your questions and provide you with a treatment plan tailored to your needs, ensuring you receive the best medical care.
Medical Team
Frequently Asked Questions
When should I see a doctor?
If you notice swelling in your abdomen or have persistent pain, it is important to consult a surgeon for evaluation.
What is abdominal eventration?
Eventration is the protrusion of abdominal organs through a defect in the abdominal wall, usually at the site of a postoperative scar.
What are the symptoms of abdominal eventration?
Abdominal bulging, pain, discomfort, and, in severe cases, nausea, vomiting, and intestinal obstruction.
What causes abdominal eventration?
Weakening of the abdominal wall after surgery, intense physical exertion, coughing, constipation, obesity, or postoperative infections.
How long does the hernia repair surgery take?
Between 1 and 2 hours for laparoscopic surgery and 2-4 hours for conventional surgery.
Is an abdominal belt necessary after surgery?
Yes, in many cases it is recommended to support the abdominal wall and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Can I prevent eventration after abdominal surgery?
Avoiding intense physical exertion, maintaining an optimal weight, and following postoperative recommendations can reduce the risk.