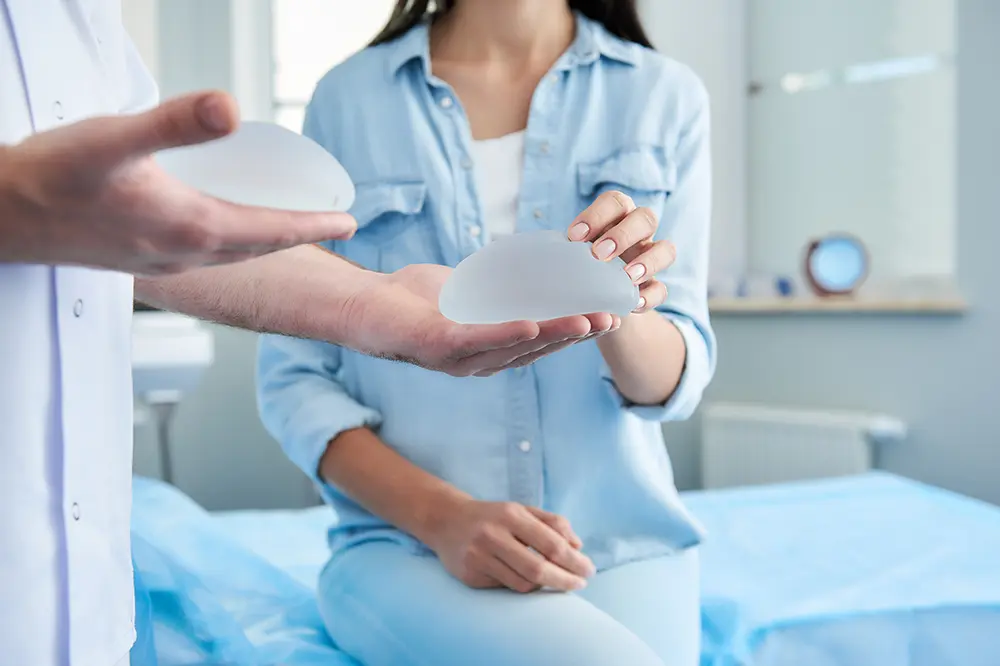
One of the most important procedures in breast cancer treatment is mastectomy, which can be total or partial. This surgery removes one or both breasts and has a profound psychological impact, as patients lose a visible symbol of femininity. For this reason, many women choose to undergo reconstructive surgery to restore their confidence and quality of life. Reconstruction can be performed immediately after mastectomy or later, once additional cancer therapies have been completed.
What Is Breast Reconstruction?
The main goal of the procedure is to restore the natural shape and size of one or both breasts after a mastectomy, during which all breast tissue, including the nipple, is removed to treat or prevent cancer. Several factors influence the choice of the most appropriate breast reconstruction technique, but there are two primary options available.
- Implants: This approach uses silicone or saline implants to recreate the breast.
- Autologous tissue reconstruction: This method uses tissue from another part of the body, such as the abdomen, back, or buttocks.
In some cases, surgeons may combine both techniques to achieve the most natural-looking results. Additional procedures are also available to reconstruct the nipple and surrounding area if they have been affected by cancer treatment.
How Do We Prepare for Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
Preparation begins with a detailed consultation to assess overall health and surgical risks. Patients are advised to stop smoking because it significantly increases the risk of complications and delays healing. Preoperative discussions also help identify the most suitable reconstructive method based on anatomy, health status, and cancer treatment history. The choice of technique is influenced by factors such as age, tissue availability, and prior therapies like radiation.
Which Breast Reconstruction Procedure Is Best for Me?
The decision depends on the patient’s medical history and personal preferences. Important considerations include breast size and shape, age, previous surgeries, smoking history, obesity, and tumor location. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully discussed with the surgeon. Individual consultation ensures a safe approach tailored to long-term health and aesthetic goals.
Breast Reconstruction With Implants
Implant-based reconstruction requires adequate skin and muscle to cover the prosthesis after mastectomy. The operation is shorter, involves less blood loss, and allows for faster recovery compared with using one’s own tissue. Silicone or saline implants are most commonly used. In many cases, this option provides a reliable and less invasive reconstruction method.
Possible Complications of Breast Reconstruction With Implants
Risks include infection, hematomas, and blood clots. Implants can rupture, leading to leakage into surrounding tissue, and scar tissue may form around them, causing hardness. There is also a rare but documented risk of developing anaplastic large cell lymphoma, a cancer of the immune system. Complications are more likely in patients with obesity, diabetes, or a smoking history, and implants do not last a lifetime, requiring regular check-ups.
Autologous Tissue Reconstruction
This technique uses tissue from areas such as the abdomen, back, or buttocks to create a new breast. The procedure takes longer than implant surgery and involves a longer recovery period. Complications may include tissue death, blood clots, or weakness at the donor site. However, breasts reconstructed with natural tissue often have a softer, more natural appearance and texture.
Recovery After Breast Reconstruction Surgery Following Mastectomy
Breast reconstruction surgery is a major surgical procedure. Whether you choose implants or reconstruction with your tissue, hospitalization may last several days. In some cases, more than one surgery may be necessary to restore the breast or breasts fully. The physical recovery usually takes up to two months, while the psychological impact of losing one or both breasts can last much longer.
During the first two months after breast reconstruction surgery, patients may experience:
- fatigue
- pain, bruising, swelling, or tenderness in the breasts and in areas where tissue was removed, such as the abdomen, back, or buttocks
- limited movement, for example, difficulty raising the arms above the head
In implant-based reconstruction, scars are usually minimal and often not visible. With autologous tissue reconstruction, however, there will also be scarring at the donor site where tissue was harvested. Pain medication is frequently prescribed during the early recovery period, and an elastic bra may be recommended to reduce swelling and provide support.
Reconstructed breasts will not look exactly like the natural ones, and sensation is usually reduced because of nerve damage. Some degree of sensitivity may gradually return over time. Today, specialists in plastic, aesthetic, and reconstructive surgery can correct a wide range of defects, improve scars, and delay the visible signs of aging. Reconstructive techniques are also valuable in the fight against cancer, helping to cure certain forms of the disease.
At VenArt Clinic, surgical procedures are performed by highly experienced doctors who have trained in leading centers in Europe, the United States, and Israel. You can learn more in the Plastic, Aesthetic, and Reconstructive Surgery section of our clinic. Schedule your consultation with us to find out the right procedure for your needs.
Medical Consultant: Dr. Claudiu Filip