The Bartholin’s glands, also called the greater vestibular glands, are important organs of the female reproductive system. Danish anatomist Caspar Bartholin Secundus first described them in 1677. Their main function is to produce mucous secretions that lubricate the vagina and vulva. The glands are located in the vestibule of the vulva, on either side of the external vaginal opening, and are approximately the size of a pea. They are homologous to the bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands).
What Is a Bartholin’s Gland Cyst?
Bartholin’s gland pathology can present as an asymptomatic mass causing vulvar asymmetry. Symptomatic masses may present with severe tenderness, surrounding redness, and edema. Ovarian cysts and abscesses commonly form in women of reproductive age and often do not require treatment. Rarely, biopsy and excision may be necessary if malignancy is suspected.
When Does a Bartholin’s Gland Cyst Occur?
Blockage of a Bartholin’s duct leads to fluid accumulation in the gland. When blocked, a Bartholin’s gland or duct cyst forms. These cysts vary in size and usually grow slowly. Infection of the gland or duct can lead to an abscess. Most Bartholin’s gland cysts are small, painless, and resolve without intervention.
What Are the Causes of Bartholin’s Cysts?
Doctors are uncertain why these glands become blocked, but infections may be caused by bacteria such as E. coli. Rarely, sexually transmitted bacteria like gonorrhea or chlamydia can be responsible. Statistics suggest that approximately 20% of women may develop a Bartholin’s gland cyst during their lifetime. Cysts most often occur around age 20, with decreasing likelihood with age.
What Are the Specific Symptoms of a Bartholin’s Gland Cyst?
Symptoms of an Uninfected Cyst
- Painless lump in the vulva area
- Redness or swelling in the vulva
- Discomfort while walking or during sexual intercourse
Symptoms of an Infected Cyst
- Pain making it difficult to sit or walk
- Fever and chills
- Swelling in the vulva
- Discharge from the cyst
How Is a Bartholin’s Gland Cyst Diagnosed?
Diagnosis can occur through patient palpation or specialist examination. Asymptomatic cysts are often unnoticed. Abscesses are identified by fever, swelling, and vulvar pain. Specialists may remove cysts in older patients to rule out malignancy or other health concerns.
Related: All About Screening and How It Helps Diagnose Cancer
Diagnostic steps include:
- Reviewing medical history
- Performing a pelvic exam
- Taking samples from the vagina or cervix to test for STIs
- Conducting a biopsy for cancer cells in patients over 40 or postmenopausal
Referral to a gynecologist specializing in gynecologic oncology may occur if cancer is suspected. VenArt Clinic offers expertise in gynecological surgery and oncology.
How Are Bartholin’s Gland Cysts Treated?
If the cyst is infected or caused by an STI, antibiotics are prescribed. Topical medications may be applied to the skin. In patients under 40 with asymptomatic cysts, treatment may not be necessary. A sitz bath may encourage spontaneous drainage: fill a bathtub with water to cover the vulva and sit gently for several sessions across 3–4 days.
Surgical Drainage of Bartholin’s Gland Cysts
The doctor creates a small incision and inserts a catheter to drain fluid. The cyst usually resolves within six weeks, and relief is immediate. Pain medication may be required for a few days. Side effects include temporary swelling, pain during intercourse, infection, bleeding, or scarring.
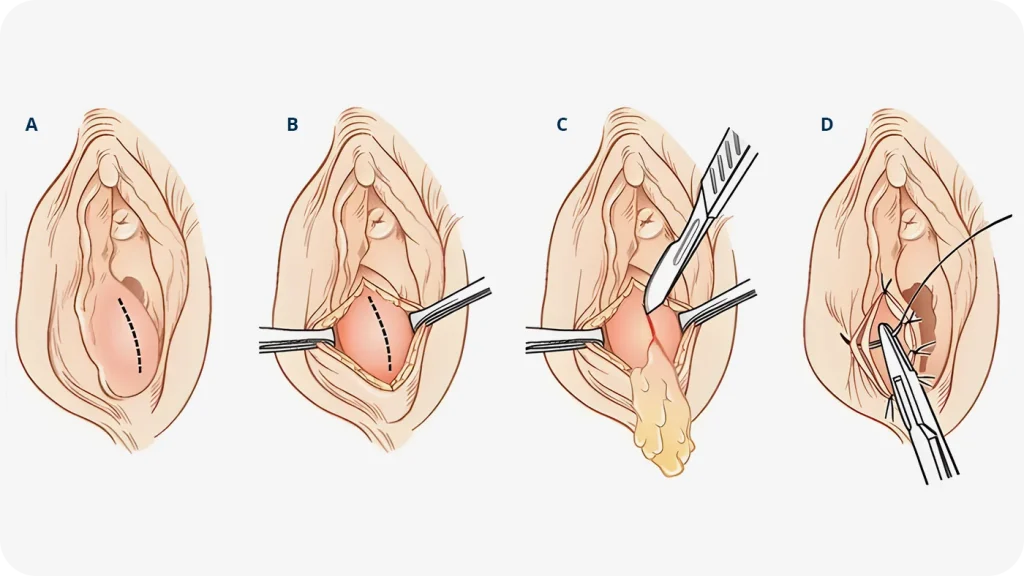
Marsupialization of Bartholin’s Cyst
If cysts recur, marsupialization forms a small pouch by suturing the cyst edges, allowing continuous drainage. The area is packed with gauze to absorb fluid and blood. The procedure takes under 30 minutes and is outpatient. Pain medication may be prescribed post-procedure, with possible risks including infection, bleeding, or recurrence.
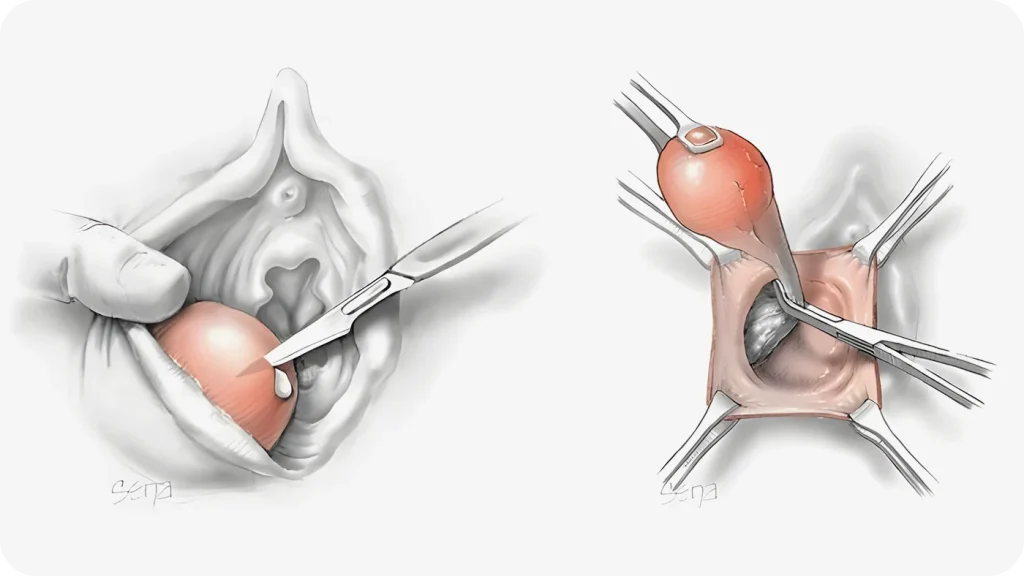
Removal of the Bartholin’s Gland
Recommended for recurrent cysts or abscesses unresponsive to other treatments. The procedure takes about an hour under general anesthesia and is outpatient. Risks include bleeding, infection, and wound complications. VenArt Clinic offers a full range of laparoscopic procedures.
Other Treatment Methods
CO₂ laser therapy can vaporize the cyst, offering safe and effective treatment. Silver nitrate ablation post-drainage is comparable to marsupialization and causes less scarring.
How Can We Prevent Bartholin’s Gland Cysts?
No method guarantees prevention. Safe sexual practices, such as condom use, reduce infection and cyst formation risk. Maintaining good hygiene lowers the chances of gland cysts and abscesses. Schedule a consultation with us and see how we can help with your condition.