Inguinal Hernia: A Major Health Problem
Groin hernia surgery is one of the most frequently performed procedures in general surgery. In the United States, approximately 700,000 cases are reported annually, while in South Korea in 2010, about 30,000 patients underwent surgery for this condition.
Various surgical procedures, both tissue-based and prosthetic, have been developed for the treatment of inguinal hernia. Despite these advancements, inguinal hernia remains a major health issue, highlighting the anatomic vulnerability of the inguinal region.
The laparoscopic approach does not change the therapeutic principles of surgery but provides a less invasive means of achieving faster patient recovery.
What Is the Endoscopic Technique TEP (Totally Extra Peritoneal)?
The TEP endoscopic technique is a complex but effective therapeutic method that ensures safe repair of the inguinal canal. It corrects the defect without breaching the abdominal wall’s integrity. This method involves placing a prosthetic mesh in the preperitoneal space, covering the entire inguinal region—including areas of indirect, direct, femoral, and obturator hernias.
It is a “tension-free” technique based on Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied at any point in a fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid. This concept is applied laparoscopically to support the mesh with evenly distributed intra-abdominal pressure.
Key benefits include minimal postoperative pain, same-day mobilization, negligible wound complications, and rapid physical recovery. A major advantage is that it avoids entry into the peritoneal cavity, eliminating the risk of injuring intra-abdominal organs such as intestinal loops.
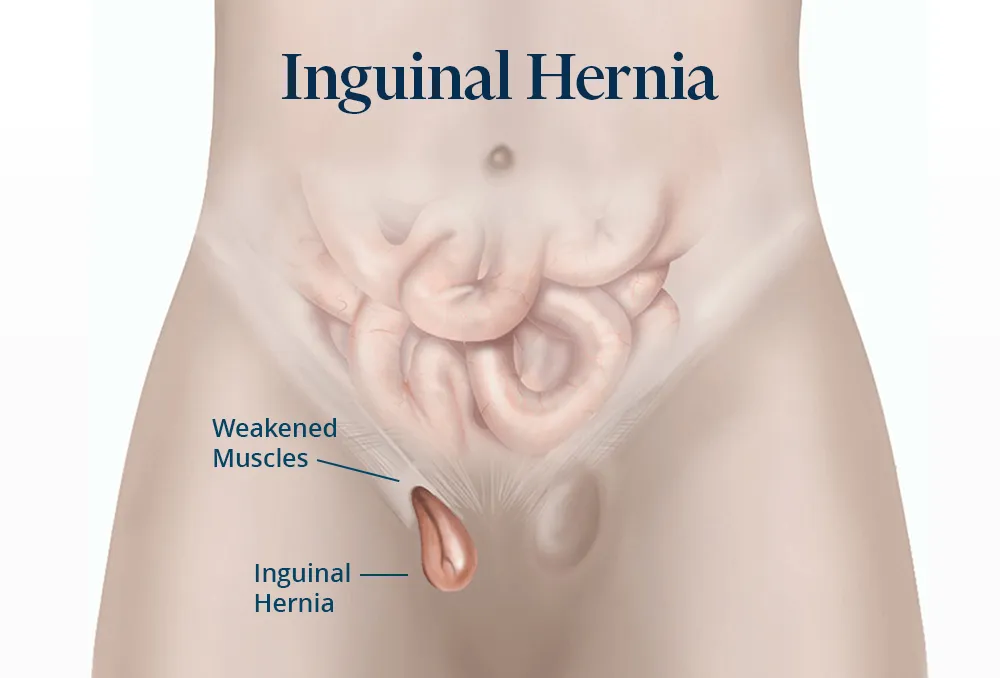
What Are the Advantages of Laparoscopic Treatment for Inguinal Hernia?
The laparoscopic method offers several significant advantages:
- A low recurrence rate of 1–4%;
- Minimal postoperative pain compared to open surgery;
- Reduced incidence of chronic pain;
- Superior aesthetic results due to smaller incisions;
- Shorter hospital stays and faster return to daily activities.
Considering these benefits, the TEP approach is increasingly regarded as a potential new “gold standard” for inguinal hernia repair.
Patient Preparation for Inguinal Hernia Surgery
Pre-operative preparation is similar to other laparoscopic surgeries. Patients undergo standard blood tests (liver and kidney function, glucose, hemogram, coagulation tests), ECG, chest X-ray, and specialty consultations if they have chronic conditions.
General anesthesia is required to maintain muscle relaxation and a stable operating field. Informed consent is obtained from all patients following a thorough explanation of the procedure and potential risks.
How Is Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Surgery Performed?
Laparoscopic hernia repair uses standard laparoscopic instruments. Three small incisions are made:
- One 12 mm subumbilical incision on the hernia side;
- One 10 mm incision on the umbilico-pubic line;
- One 5 mm suprapubic incision.
These incisions accommodate three working trocars (2 x 10 mm, 1 x 5 mm)
The dissection plane lies just behind the rectus abdominis muscle in an avascular layer. After isolating the hernia sac and repositioning the spermatic cord and peritoneum, the surgeon protects the area with a 15×10 cm polypropylene mesh.
The new polypropylene prostheses are manufactured in variable dimensions, designed to match the contour of the inguinal canal wall. This anatomical shape makes them easier to handle and place precisely at the site of the hernia. The TEP technique continues to be one of the most widely used and reliable methods for repairing inguinal hernias.
Selecting this surgical approach requires the surgeon to possess an advanced level of expertise in laparoscopic surgery. Because the properitoneal space is less familiar compared to the intraperitoneal cavity—well known to most general surgeons—the TEP technique demands a significantly longer learning curve to master.
Once this technique is fully mastered and the anatomy of the properitoneal space is clearly understood, the PET approach becomes a much faster and more efficient method for resolving inguinal hernias. It remains a highly safe and effective technique, offering excellent results in the short, medium, and long term—along with the major benefit of eliminating the risk of injury to intra-abdominal organs.
What Can We Eat Before Inguinal Hernia Surgery?
Preoperative dietary guidelines advise patients to avoid foods and drinks that may cause abdominal bloating due to fermentation. Patients should refrain from eating such items the day before surgery. On the day of the procedure, no food or fluids are allowed.
Hernia Surgery and Antibiotic Prophylaxis
According to European Association of Endoscopic Surgery (EAES) guidelines, prophylactic antibiotics are not required for laparoscopic hernia repair in healthy patients. Exceptions include patients who are immunocompromised, diabetic, undergoing cancer treatment, or those with prosthetic heart valves.
How Does an Inguinal Hernia Affect Sex Life?
Sexual function is generally unaffected by inguinal hernia or its surgical repair. In rare cases where the hernia is incarcerated, the spermatic cord or testicular blood vessels may be compromised, leading to reduced sperm transport or testicular atrophy, which can affect fertility.
Modern surgical techniques greatly minimize these risks. However, pain and swelling before surgery may temporarily interfere with sexual activity.
About VenArt Clinic
At VenArt Clinic Cluj, you will find highly trained specialists across several disciplines including ENT surgery, vascular surgery, general surgery, gynecologic oncology, plastic and aesthetic surgery, and diagnostic ultrasound.
We are proud to collaborate with renowned French vascular specialist Dr. René Milleret, whose innovative and minimally invasive treatments for varicose veins are now also available in Bucharest through VenArt Clinic.
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery Cluj.
Phone appointments: (+40) 731 837 520