Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Effective solutions for relieving Quervain's tenosynovitis
Home » Orthopedic Surgery » Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Conditions Treated
Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a painful condition that affects the tendons in the wrist, particularly in the thumb area.
If you are experiencing pain or difficulty moving, find out how you can manage your symptoms and what treatment options are available.
Book an Appointment
What is Quervain's tenosynovitis?
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a chronic inflammation of the tendons that control the movement of the thumb (index finger) – the short extensor tendon and the long abductor tendon. This condition occurs due to thickening of the tendon sheath, which prevents normal sliding of the tendon and causes pain when extending the thumb and grasping objects.
This inflammation leads to pain and discomfort in the wrist area, making normal movements difficult.
Causes of Quervain's tenosynovitis
This condition is caused by overuse of the tendons, and the main causes include:
Repetitive movements of the hand and thumb (e.g., typing, using a mouse, knitting, playing musical instruments, professional activities such as sewing or construction);
- Injuries to the wrist, such as sprains or fractures;
- Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that affects the joints and tendons;
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, which can increase the risk of inflammation.
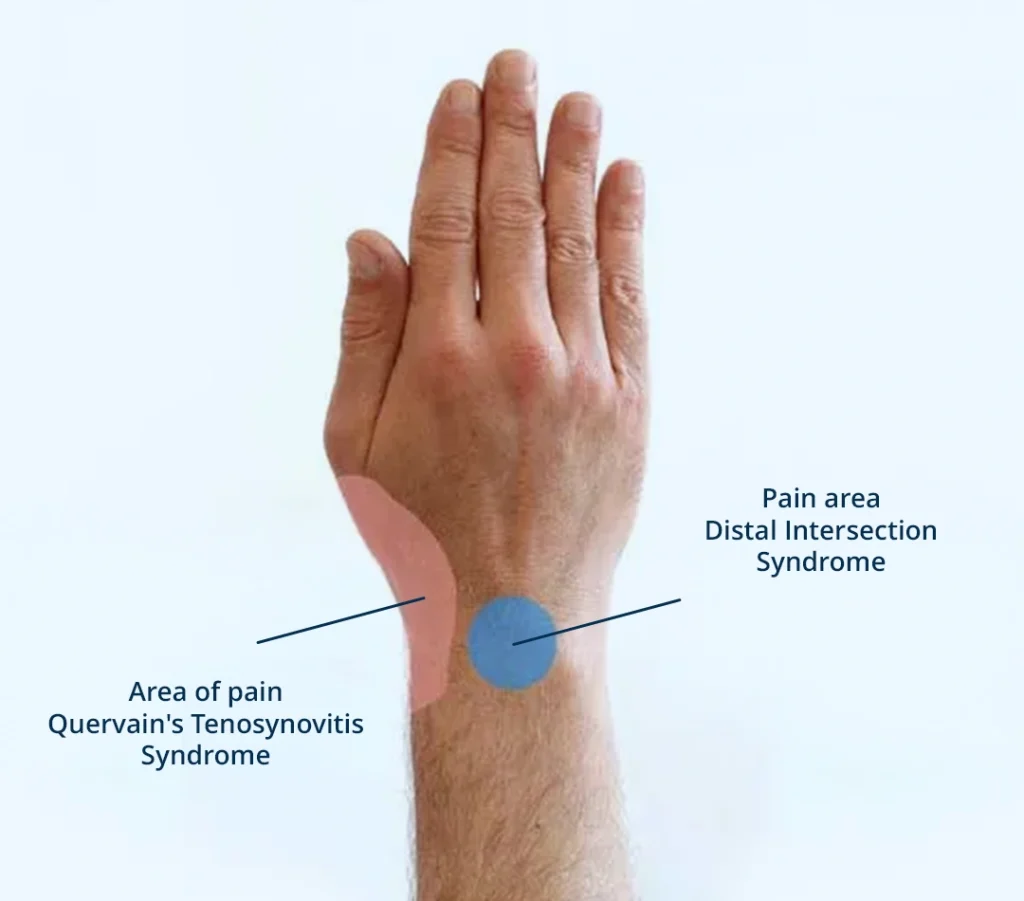
Symptoms of Quervain's tenosynovitis
- Pain at the base of the thumb, which may be sharp or dull, constant or intermittent;
- Swelling and tenderness in the affected area;
- Difficulty moving the thumb and wrist;
- A cracking sensation when moving the thumb;
- The pain may radiate to the forearm.
If symptoms persist and affect daily activities, minimally invasive surgical treatment may be considered.
At VenArt Clinic, the procedure involves releasing the tendon sheath, thereby reducing friction and pain and ensuring a quick and effective recovery.
Diagnosis of Quervain's tenosynovitis
The doctor can diagnose this condition by:
- Physical examination: palpating the affected area and identifying painful points;
- Finkelstein test: the patient bends their thumb into their palm, covers it with their other fingers, and rotates their wrist toward their little finger. If this movement causes pain, the test is positive;
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound: can be used to confirm tendon inflammation.
Quervain's tendinitis treatment
Conservative treatment
- Rest: avoiding repetitive movements that aggravate inflammation;
- Immobilization: using a brace to keep the thumb and wrist in a fixed position;
- Anti-inflammatory medications: ibuprofen, naproxen to reduce inflammation;
- Corticosteroid injections: can reduce inflammation quickly, but should be used with caution.
Physical therapy and exercise therapy
- Manual therapy techniques to reduce pain;
- Exercises to improve mobility and flexibility;
- Electrotherapy and ultrasound to stimulate tendon recovery.
Surgical treatment
- If symptoms persist and conservative treatments are ineffective, tendon sheath release surgery may be recommended, a minimally invasive procedure that creates more space for the tendons and eliminates compression.
Brace for Quervain's tenosynovitis
- A brace for Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a device that immobilizes the thumb and wrist, reducing pressure on the affected tendons.
- It is recommended to wear it for 4-6 weeks, especially in the acute phase, to relieve pain and facilitate healing, as it is an effective non-surgical option.
- Consult a doctor for adjustment and exact duration.
Recovery and prevention
- After treatment, recovery exercises are essential for restoring mobility;
- Adapting the working environment: using ergonomic equipment to prevent wrist strain;
- Taking regular breaks from repetitive activities to reduce the risk of inflammation recurring.
Quervain’s tenosynovitis can affect your quality of life, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, recovery is possible. If you experience the symptoms described, consult a specialist for a personalized treatment plan.
Why choose VenArt Clinic?
- Team of specialized doctors with extensive experience;
- Modern technology and innovative methods;
- Minimally invasive treatments for rapid recovery;
- Personalized approach for each patient;
- Proven results and numerous successful cases in orthopedic surgery;
- Warm and professional atmosphere;
- Complete services in one location.
Schedule an appointment now!
Find out how you can manage your symptoms and what treatment options are available.
Our specialists will answer all your questions and provide you with a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Medical Team
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Quervain's tenosynovitis?
It is an inflammation of the tendon sheath at the base of the thumb, caused by repetitive movements, which causes pain and difficulty in movement.
What are the symptoms of Quervain's tenosynovitis?
Pain at the base of the thumb, swelling, tenderness, and sometimes a “catching” sensation when moving the wrist or thumb.
What causes Quervain's tenosynovitis?
Repetitive activities (e.g., typing, sewing), frequent heavy lifting, or hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy).
Can I treat Quervain's tenosynovitis without surgery?
Yes, with rest, splints, anti-inflammatory drugs, or injections; surgery is the last resort.
How is Quervain's tenosynovitis diagnosed?
Through physical examination, including the Finkelstein test (bending the thumb over the palm), and sometimes ultrasound.
When is surgery necessary for Quervain's tenosynovitis?
When non-surgical treatments (rest, splints, corticosteroid injections) do not reduce pain after 4-6 weeks.
How does surgery for Quervain's tenosynovitis work?
A small incision is made to release the tendon sheath under local anesthesia; the procedure takes about 15-30 minutes.
Are there any risks associated with the surgery?
Minimal risks: infection, nerve damage, or stiffness; complications are rare with an experienced surgeon.
How can I prevent Quervain's tenosynovitis from recurring?
Avoid repetitive movements, use ergonomic equipment, and perform hand stretching exercises.