Introduction
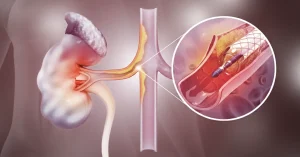
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat aortic aneurysms, most commonly abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). When the procedure is used to treat thoracic aortic aneurysms, it is called TEVAR.
The EVAR procedure
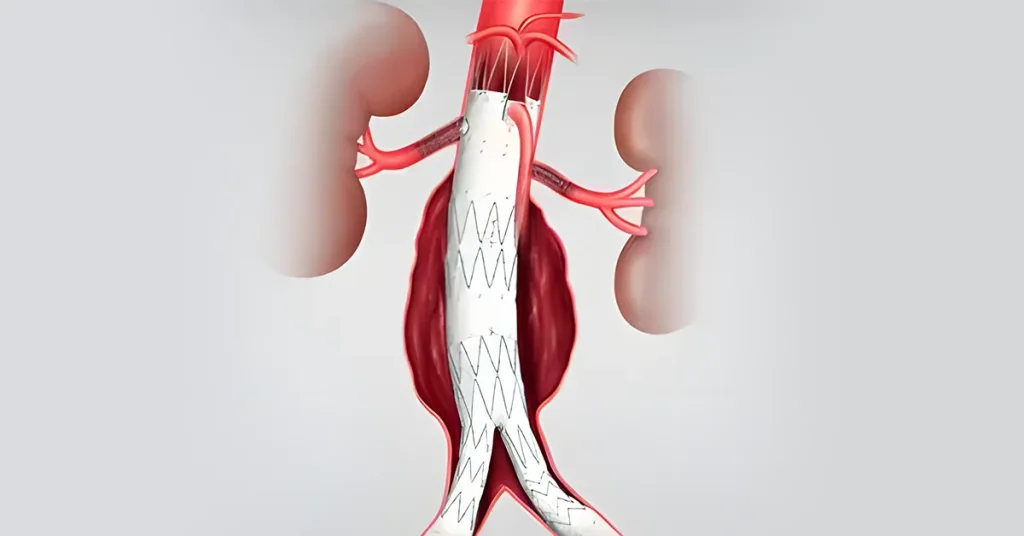
EVAR (Endovascular Aortic Repair) involves placing an expandable prosthesis inside the aorta to treat aortic disease without performing traditional aortic aneurysm surgery.
It has become the most common technique for repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms, surpassing open surgery due to its reduced risks and rapid recovery.
Medical Uses
EVAR is suitable for aneurysms that start below the renal arteries and have a normal aortic length suitable for endograft fixation.
Patients with aneurysms require elective repair when the aneurysm reaches a diameter of more than 5.5 cm or grows rapidly. Other indications include aneurysms that cause pain or embolisms. There are also complex types of EVAR, where the prosthesis is placed above the level of the renal arteries and involves a fenestrated EVAR, so that the renal arteries pass through these intentionally left windows.
In most EVAR procedures, the prosthesis must be customized in advance to fit the patient’s anatomy.
Advantages of the EVAR Procedure
Minimally invasive: The procedure is less invasive than open surgery, reducing risks and recovery time.
Reduced Risk of Complications: Studies have shown that EVAR has fewer early complications compared to open surgery.
Advanced Technology: Technological improvements in stent design have reduced the need for secondary procedures to repair endoleaks and other problems.

Contraindications and Considerations
The patient’s anatomy may be unsuitable for EVAR in certain cases, such as short proximal aortic necks or aneurysmal iliac arteries. EVAR may be contraindicated or associated with complications in cases of hostile aortic necks.
Recovery after aortic aneurysm surgery
Your hospital stay after the procedure usually lasts 2 or 3 days. While your recovery will take less time than recovery from open-chest thoracic aneurysm surgery, early restrictions are similar and include:
- Do not drive until your doctor approves (usually within 1–2 weeks after the procedure and you are no longer taking pain medication);
- No baths until the incisions have healed; showers and sponge baths around the incision are allowed;
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for approximately 4–6 weeks after the procedure.
You will return for a follow-up visit within one month of the procedure. Follow-up imaging tests will take place at 1 and 6 months after the procedure to ensure that the stent is functioning properly.
At VenArt Clinic, we are dedicated to providing our patients with the most advanced care in EVAR so that you can live a long and healthy life.
Consulting physicians: Prof. Dr. Jérôme Cau and Dr. Marius Fodor